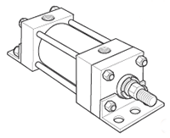
Parker Air Cylinder Mounting Information
Parker single-rod air cylinders are available in 20 standard mounting styles. Stroke length, piston rod diameter and the method of connection to load are all important factors to consider when selecting an air cylinder for an application, as these factors will effect the cylinder's operation and service life.
Each style falls into one of three basic groups:
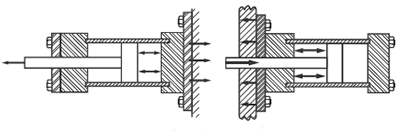
Group 1 - Straight line force transfer with fixed mounts that absorb force on the cylinder centerline.
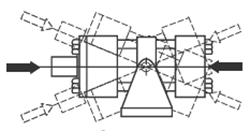
Group 2 - Pivot force transfer with pivot mounts that absorb force on cylinder centerline and permit cylinder to change alignment in one plane.
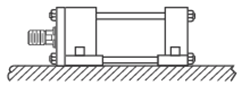
Group 3 - Straight line force transfer with fixed mounts that do not absorb force on the cylinder centerline.
Straight Line Force Transfer (Group 1)
Fixed mount, centerline force-absorbing cylinders are considered ideal for straight line force transfer. The symmetrical mounts allow the thrust and tension forces of the piston rod to be distributed uniformly and keep damage from cylinder bearing sideloading to a minimum.
|
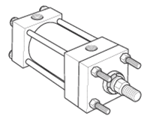
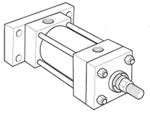
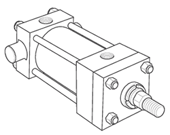
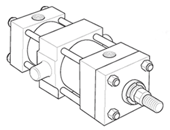
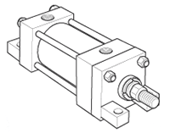
Styles TB, TC & TD - Tie Rods Extended
|
|
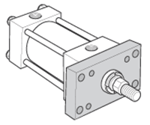
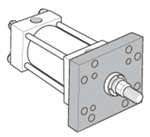
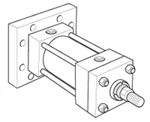
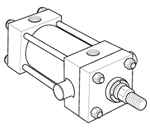
Styles J, JB, H & HB - Flange Mount
|
Pivot Force Transfer (Group 2)
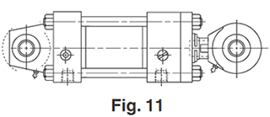
Pivot mounted cylinders absorb force on the centerline and should be used in applications where the machine member travels in a curved path. Clevis or trunnion mounting provides a pivot point for the cylinder to move during the work cycle.
|
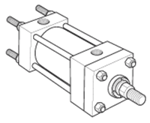
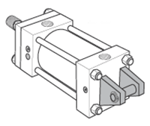
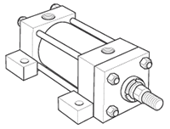
Styles BB, BC, SB, D, DB & DD - Pivot Mount
|
Straight Line Force Transfer (Group 3)
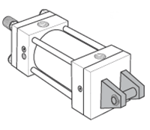
Side mounted cylinders do not absorb force on the centerline and have mounting lugs connected to the ends. These cylinders should be specified with a stroke length at least equal to the bore size.
|
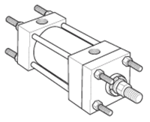
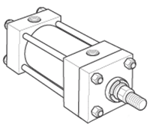
Styles C, CB, F, TEF & G - Side Mount
|
Available Pneumatic Cylinder Styles
 |
Tie Rod Cylinders |  |
Guided Cylinders |
 |
Round Body Cylinders |  |
Rodless Cylinders |
 |
Compact Cylinders |
 |
 |
Engineering & Product Selection Information
Pneumatic Product Selection
- Pneumatic Actuators & Air Cylinders
- Pneumatic Cylinders
- Automation Products: rotary actuators, grippers, slide tables, rotary tables, escapement
- Actuator Accessories: Linear alignment couplers, flow controls, air oil tanks, rodlocks, electronic sensors, shock absorbers
Application Engineering Data
- Operating Principles and Construction
- Fluids and Temperature
- Push and Pull Forces
- Mounting Information
- Ports
- Tie Rod Supports, Stroke Data & Stroke Adjusters
- Mounting Classes
- Stop Tubing
- Stroke Selection Chart
- Deceleration Force and Air Requirements
- Cushion Ratings and Air Requirements
- NFPA Rod End Data and Piston Rods
- Modifications, Special Assemblies, Tandem Cylinders, Duplex Cylinders
- Rotary Actuator Torque Requirements
- Rotary Actuator Basic Equations
- Conversion Factors