The information below covers the chemical compatibility of Parker plastic tubing listed in Parker Parflex Catalog 4660, Edition 8/2014 (Thermoplastic & Fluoropolymer Products). This chemical compatibility guide must not be used in conjunction with any other compatibility guides from previous or future catalog editions, bulletins or publications. Plastic tubing chemical compatibility may change from time to time due to changes in manufacturing process. Incorrect use of these charts could result in personal injury, death or property damage.
| Parker Thermoplastic Tubing | Core Material | Code |
| HDPE | High Density Polyethylene | HDPE |
| N | Flexible Nylon | N |
| NR | Unplasticized Nylon (semi-rigid) | NR |
| E | Linear Low Density Polyethylene | PE |
| PEFR | Flame Resistant Polyethylene | PEFR |
| PP | Polypropylene | PP |
| PV | Flexible Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | PV |
| U, HU | Polyurethane | U |
| Parker Fluoropolymer Tubing |
Core Material | Code |
| 103, 203, HS1.3FEP, HS1.6FEP | Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene | FEP |
| 104, 204 | Perfluoroalkoxy | PFA |
| TFL, TFS, TFT, TFH, 101, 201, TFB, HS2TFS, HS2TFT, HS2TFL, HS2TFI, HS4TFI | Polytetrafluoroethylene | TFE |
| 110,111 | Polyvinylidene Fluoride | PVDF |
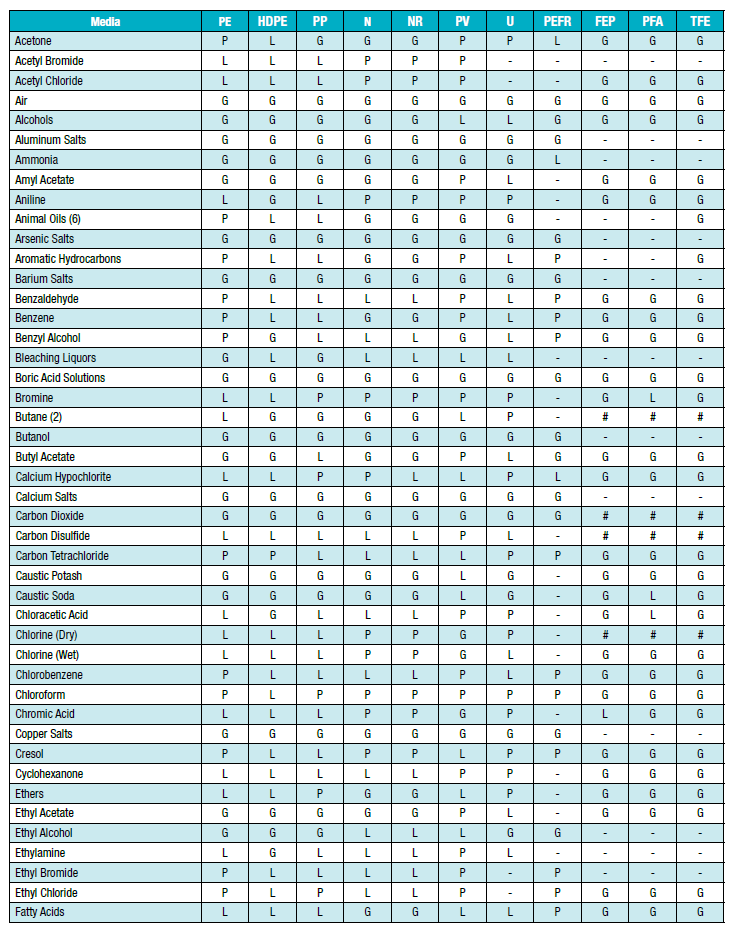
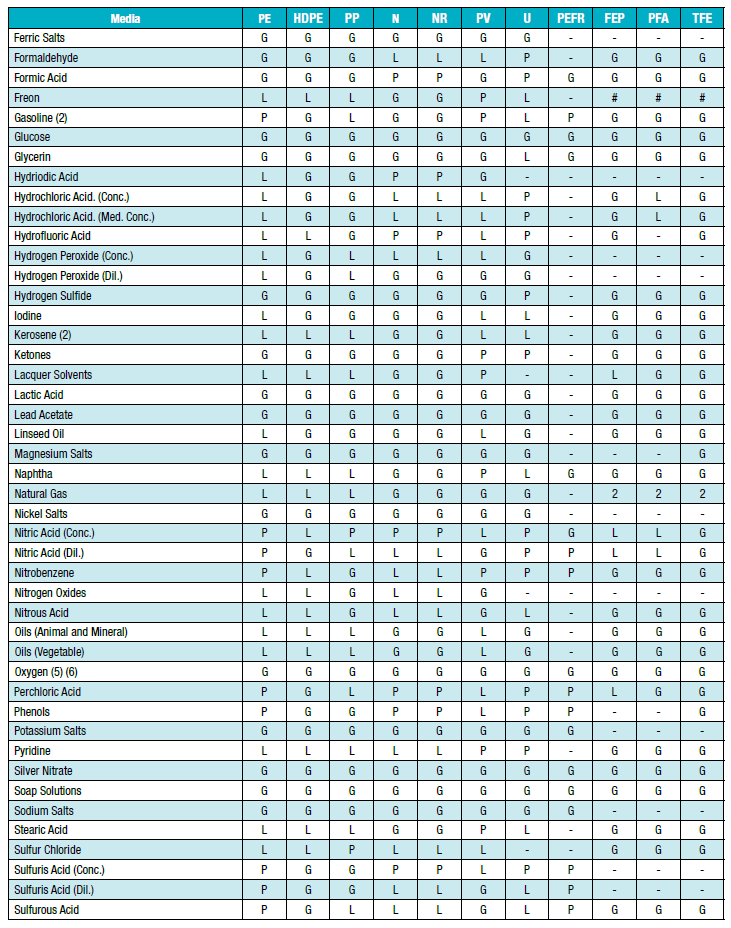
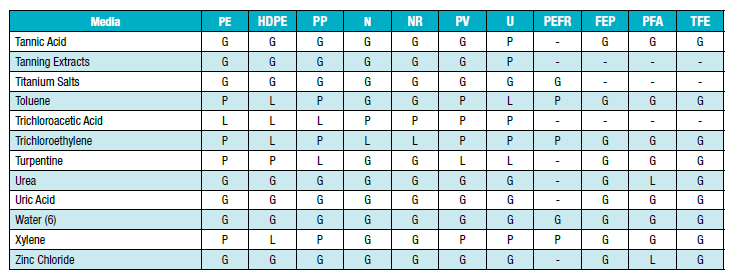
| G | Good to Excellent - Little or no swelling, tensile or surface changes. Preferred choice. |
| L | Marginal or Conditional - Noticeable effects but not necessarily indicating lack of serviceability. Further testing suggested for specific applications. Long-term effects such as stiffening or potential for crazing should be evaluated |
| P | Poor or Unsatisfactory - Not recommended without extensive and realistic testing. |
| - | Not tested - Compatibility not known |
| # | For fluoroplolymer - Indicates good chemical resistance but potential for excessive permeation. |